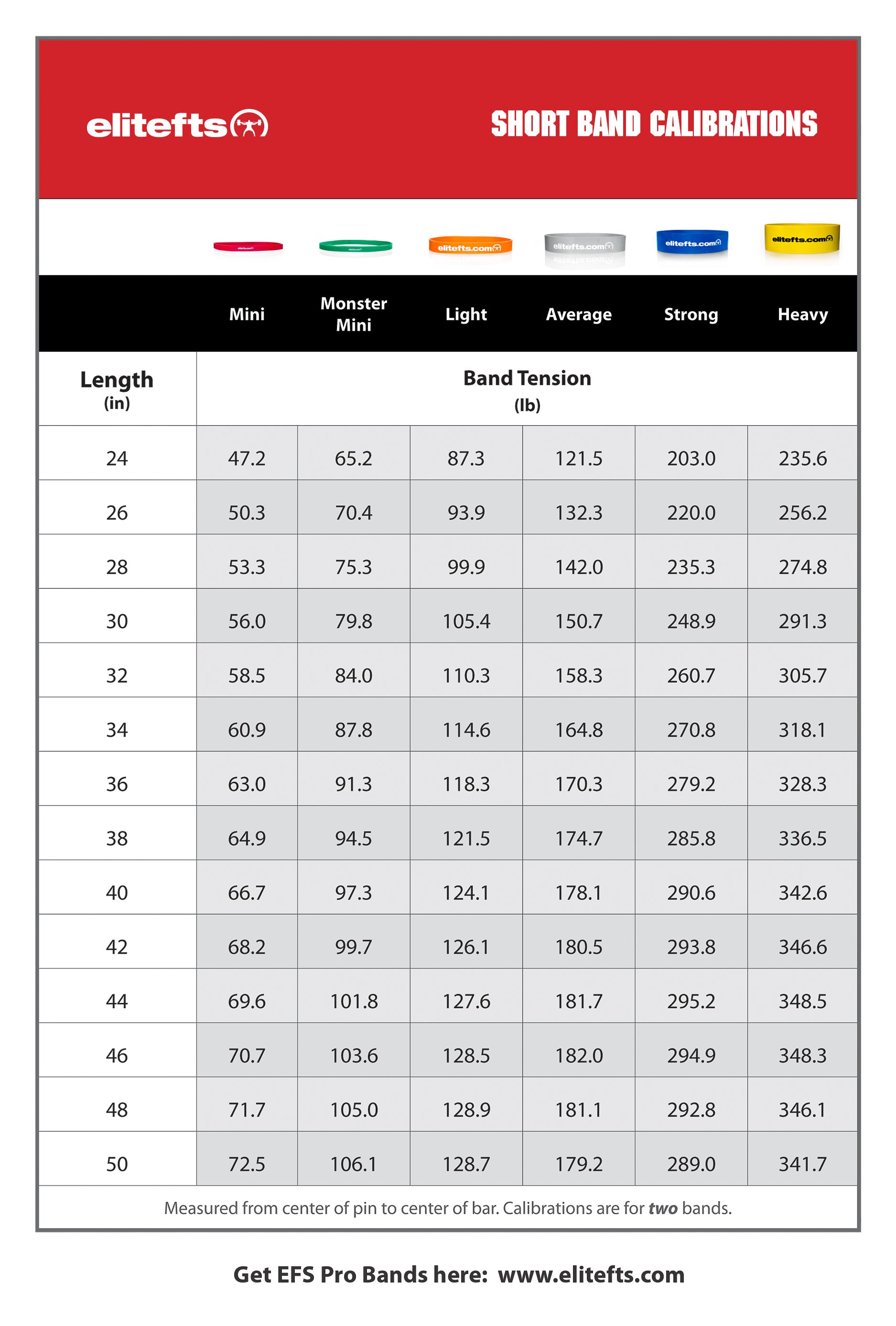
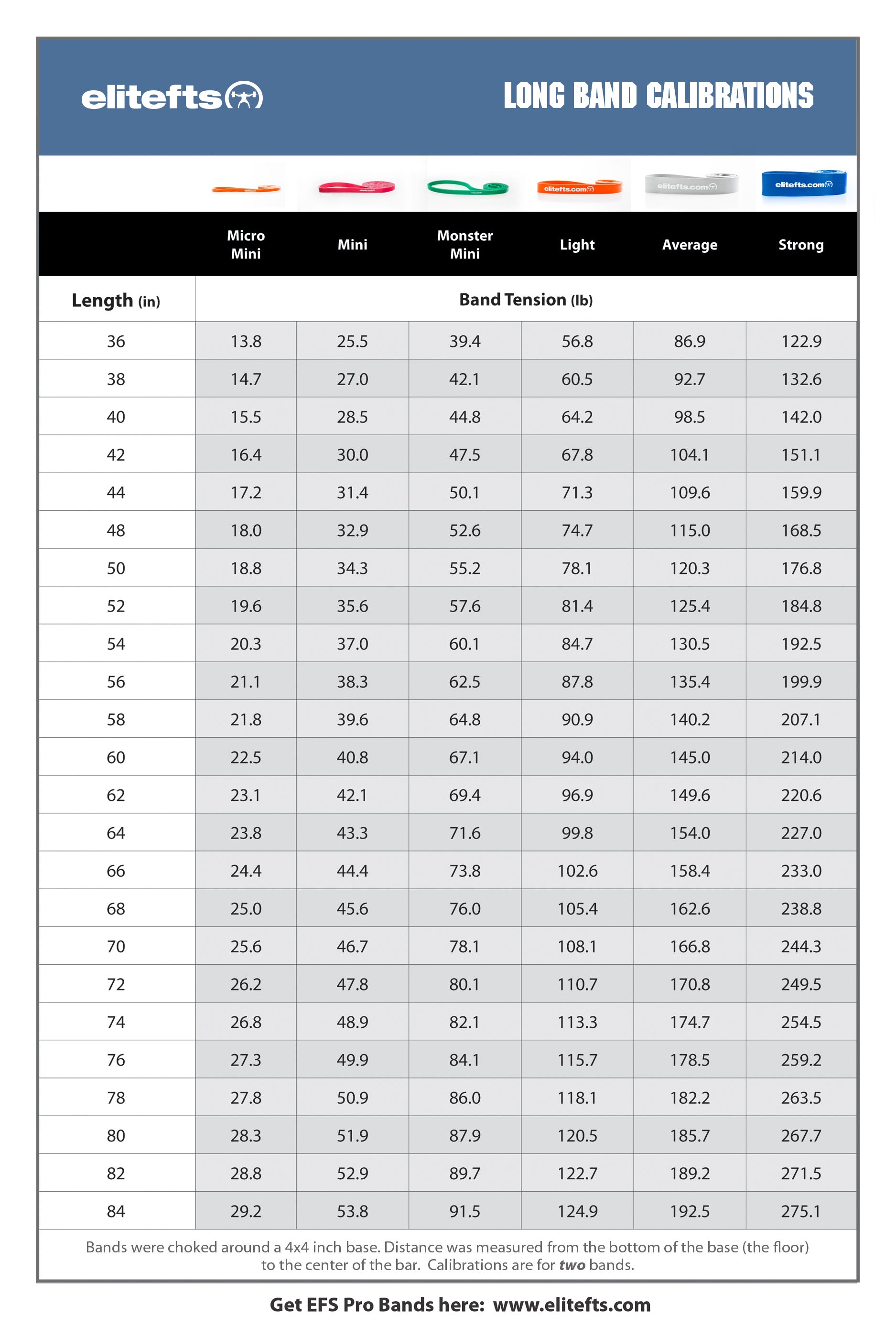
Originally published in December of 2003
What is the basic template for bench press training? Wednesday: Max effort bench press training 1. The max effort exercise: work up to 1 or 3 rep max 2. Supplemental exercise: Triceps movement The best exercises for this group include JM presses, and barbell or dumbbell extensions, board presses or rack lockouts. 3. Accessory movements: (triceps, lats, delts) • This includes movements for the lats, shoulders and possibly extra tricep work. The best movements for this group include tricep extensions, rows, and various shoulder raises. 4. Prehabilation Movements: (training of the joints) • This includes movements for the elbow and shoulder joints: The best movements for this group include external shoulder rotations, pushdowns andsled dragging for two to four sets of 12 to 15 reps. Sunday: Dynamic bench press training 1. Bench Press: Work up to 8 sets of 3 reps using three different grips all inside the rings. 2. Supplemental Exercise: Triceps movement The best movements are close grip bench presses, JM presses, and dumbbell or barbell extensions, high board presses, or rack lockouts. 3. Accessory movements: (triceps, lats, delts) • This includes movements for the lats, shoulders and possibly extra tricep work. The best movements for this group include tricep extensions or pushdowns, rows and various shoulder raises. 4. Prehabilation Movements: (training of the joints) • This includes movements for the elbow and shoulder joints. The best movements for this group include external shoulder rotations, press downs and sled dragging for two to four sets of 12 to 15 reps. What is the Basic Template for squat/deadlift workouts? Monday: Max effort squat and deadlift training 1. The max effort exercise: work up to 1 to 3 rep max 2. The supplemental movement: • This will include one exercise for the hamstrings. The best movements for them include partial deadlifts, stiff leg deadlifts, Romanian deadlifts and
glute ham raises for three to six sets of 5 to 8 reps. 3. The accessory movements: • One or two abdominal movements • One lower back movement: The best exercise for this purpose is the reverse hyper for three to four sets of 6 to10 reps. 4. Prehabilation Movements • This can include exercises for the knee and hip joints. The best movements for this purpose include any type of lower body sled dragging. Friday: Dynamic squat and deadlift training 1. The box squat: Work up to 8 sets of 2 reps with prescribed percentage 2. The supplemental movement: • This will include one exercise for the hamstrings. The best movements for the hams include partial deadlifts, stiff leg deadlifts, Romanian deadlifts and glute ham raises for four to six sets of 5 to 8 reps. 3. The accessory movements: • One or two abdominal movements for three to five sets of 6 to 12 reps. One lower back movement: The best exercise for this purpose is the reverse hyper performed for three to four sets of 8 reps. 4. Prehabilation Movements • This can include exercises for the knee and hip joints. The best movements for this purpose include any type of lower body sled dragging. What are the percentages to use on dynamic bench day? The percentages for dynamic bench press day when using straight weight (no bands or chains) or chains are as follows:
- Beginner - 60%
- Intermediate - 55%
- Advanced - 50%
author of Supertraining) and Louie Simmons the topic of periodization training came up. Mel made a statement that I will never forget. He told us of a comment that was told to him by Medvedyev one of the originators of the periodization concept. This comment was that periodization training in the United States has been set back 40 years by some of the current books written on the topic. Not only will the progressive overload style of training lead to overtraining and stagnation it also ignores one basic concept of training, increasing work capacity. Work capacity it the underlying component of any training program. It is the ability to perform work, which determines your level of fitness that in turn will determine your level of preparedness. If you raise your work capacity too fast you will overtrain and if you reduce it under your current level you will digress. If your work capacity is still at the same level it was two years ago then I will bet you are at the same strength and hypertrophy level you were to years ago. You can increase your work capacity by several means described below. Extra Training Sessions: There are several types of extra workouts that can make a tremendous difference in your training. Overseas it is not uncommon to see athletes performing up to 3 to 4 workouts per day. These workouts can be designed for a number of reasons. Recovery Workouts: These training sessions may also be known as feeder workouts and are designed to aid in the recovery process. For example, if you performed a heavy bench press workout on day one with 400 pounds then on day 2 you would use the same exercise with very light weight for higher repetitions such as 135 for 2 sets of 20 to induce blood into the muscle to speed the recovery process. Another type of feeder or recovery workout and the one most used a Westside barbell is with the use of a dragging sled. The dragging sled has helped are lifters with a multiple of training situations. We have seen the use of the sled add 30 to 60 pounds on one’s deadlift, aid in the recovery process, add lean body mass, and bring up weak points. The sled can be used for a number of different exercises for both the upper and lower body. Some of these include around the waist dragging, ankle dragging (drag the sled with the use of your ankles), pull through dragging (drag the sled by holding the sled strap between your legs), and upper body dragging (drag the sled by performing front raises, rear raises, side raises, presses and extensions). These sled exercises are best used with the empirical rule of 60%. This basically means that on the first day you choose the heaviest weight you will use for that exercise and decrease the weight by 60% for each day after that for three days. After that point, you repeat the process. This rule is essential for avoiding stagnation with any given exercise. A great benefit of the sled is for many of the exercises there is no eccentric motion. It is believed that the eccentric is responsible for DOMS (delayed onset muscle soreness). When the eccentric is taken away from the exercise you are left with a concentric motion that will induce blood flow to the muscle without causing DOMS. What are the percentages to use on dynamic squat day when using chains or straight weight? When using
chains or straight weight, the percentages are as follows: Beginner:
- Week 1: 63% for 10 sets of 2 reps
- Week 2: 65% for 10 sets of 2 reps
- Week 3: 68% for 10 sets of 2 reps
- Week 1: 60% for 8 sets of 2 reps
- Week 2: 63% for 8 sets of 2 reps
- Week 3: 65% for 8 sets of 2 reps
- Week 1: 55% for 8 sets of 2 reps
- Week 2: 58% for 8 sets of 2 reps
- Week 3: 60% for 8 sets of 2 reps
- Squat Max 200-400 Pounds = 60-pound chain
- Squat Max 400-500 Pounds = 80-pound chain
- Squat Max 500-600 Pounds = 100-pound chain
- Squat Max 600-800 Pounds = 120-pound chain
- Squat Max 800-900 Pounds = 160-pound chain
- Week 1: 47% 8 sets of 2
- Week 2: 51% 8 sets of 2
- Week 3: 53% 8 sets of 2
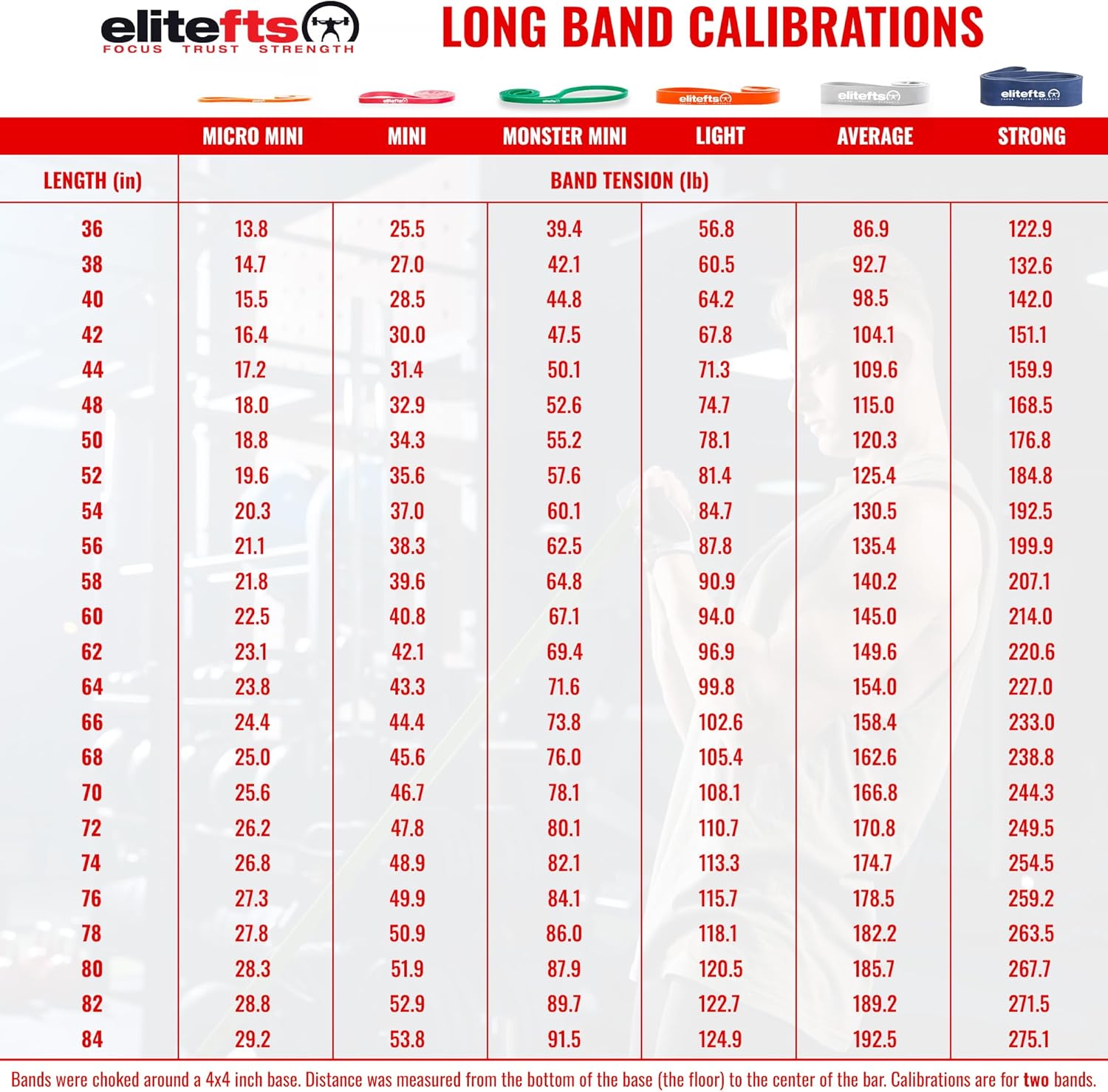
- 300-500,
Light band - 501-750,
Average band - 751-1000,
Strong band
- You can sit back further when
box squatting. This places more stress on the posterior chain muscles. Also, this puts less stress on your knees and will allow an athlete to train that may have had surgery or a previous knee problem. - You always know how low you're going. If you want to squat two inches below parallel then set your box up at that height. This way your body will always sit as low as it's conditioned. If you want to squat one inch high, then set the box higher.
- It allows a lifter that has poor flexibility or weak hamstrings to squat correctly. Many times an athlete that has either of the above problems cannot free squat without the coaches and trainers cringing. By putting this athlete on an above parallel box it allows for a great workout. Make sure you take extra steps to strengthen the hamstrings and address the flexbility problem.
- Squatting on a box breaks the eccentric/concentric chain. This is one of the best ways to develop explosive strength. Fourth, the box is great for teaching proper squatting technique. Most athletes and lifters have very poor squat technique because of bad coaching, muscle imbalances, and flexibility. The box can work as a great aid to teaching the proper way to sit back into a squat.
- You can squat lower when using a box.
- You can correct mistakes at the bottom of a box squat. This is something impossible to do when performing a free squat.
- It's easier to teach someone how to squat when using a box.
- Your recovery between squat sessions is improved.
bar out of the
rack, the hands must be evenly placed on the bar. Secure the bar on the back where it feels the most comfortable. To lift the bar out of the rack, one must push evenly with the legs, arch the back, push your abs out against the belt, and lift the chest up while driving the head back. A high chest will ensure the bar rests as far back as possible. Slide one foot back, then the other, to assume a position to squat. Set your feet up in a wide stance and point your toes straight ahead or slightly outward. Also, keep your elbows pulled under the bar to ensure tightness in the upper back. When you’re ready for the descent make sure to keep the same arched back position. Pull your shoulder blades together and pull as much air into your stomach as possible. Again, push your abs out. You’ll maintain this tightness throughout the set. To begin the descent, push your hips back and push your knees out to the sides to ensure maximum hip involvement. Once you reach the box, you need to sit on it and release the hip flexors while keeping the back arched and abs pushed out. At the same time, drive your knees out to the side. To begin the ascent, keep pushing out on the belt, arch the back as much as possible, and drive the head, chest, and shoulders to the rear. If you push with the legs first your buttocks will raise first, forcing the bar over the knees and causing stress to the lower back and knees, thus diminishing the power of the squat. You need to keep the barbell in a direct line with the heels throughout the entire movement and this can only be done by keeping your back arched. What is General Physical Preparedness (GPP) and why should I care about it? GPP is intended to provide balanced physical conditioning between all the fitness components such as flexibility, strength, endurance, speed, and other factors. According to Yuri Verkhoshansky in
The Fundamentals of Special Strength Training in Sport and as outlined in Supertraining by Mel C Siff, there are several functions of GPP:
- To strengthen or restore motor skills, which play an auxiliary role in perfecting sports ability.
- To teach abilities developed insufficiently by the given sport; increase the general work capacity or preserve it.
- To provide active rest, promote restoration after strenuous loading, and counteract the monotony of training.
A cambered bench bar has a four-inch camber in the middle of it to allow for greater range of motion. There are right and wrong ways to use this bar and the style you use is dependent on your own flexibility and ability to use the bar. The first way is to take the bar down to your chest, which I believe works dynamic flexibility but is only beneficial with very lightweight. I don’t believe the heavy work should be taken all the way down to the chest because of the excess shoulder rotation. The best way to use this bar is to bring it down to a point where it’s only about a half inch lower than where a regular bar would be. This way you won’t be getting any type of reflex off the chest. The last way to do this is with the use of boards to control how low the bar will go. Use two to three inches of boards so you can control how deep the bar will travel. Ultra Wide Bench Presses Ultra wide grip bench presses is simply a wide-grip bench press outside your widest grip. For most people, this would be with your forefinger on the rings. This isn’t a good movement to use for a one-rep max because of the stress it puts on the shoulders. It’s best done working up to two heavy sets of five or six reps. How long can I use the bands on the bench press? This is entirely up to the individual, but using
bands for every workout is not advised. Here are some suggestions on how to cycle bands during your dynamic bench cycle.
- Alternate bands and straight weight every week.
- Alternate bands and chains every week.
- Three weeks of bands followed by three weeks of straight weight or chains.
-
2-board press -
3-board press -
4-board press - Floor press
- Incline press
- Reverse band press
- Cambered bar press
- Safety squat bar suspended in chains
- Cambered bar suspended in chains
- Cambered bar good mornings
- Good mornings
- Deadlift standing on mats (about 4” off the ground)
- Deadlift off pins in a power rack
- Reverse band deadlift
- Deadlift pulling against bands (works well with the Jump Stretch platform)
- Safety squat bar
- Cambered squat bar
- Manta Ray squat
- Front squat with front squat harness